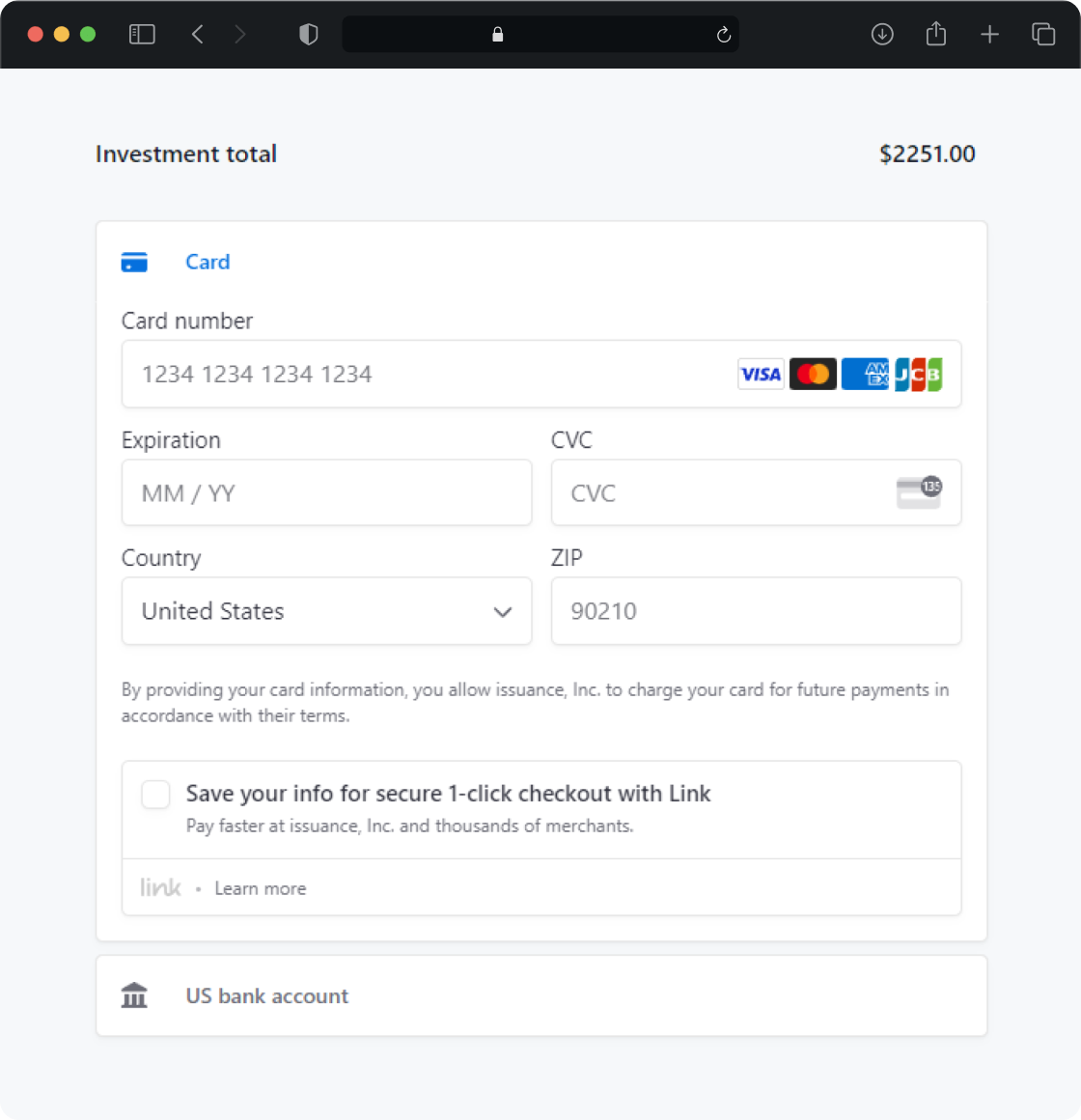
Meet issuance express
Optimized for Regulation CF, Issuance Express offers a high quality fundraising and investing experience.
What is regulation crowdfunding?
Raise up to $5M
Regulation CF allows qualified Issuers to raise up to $5M.
See the disclosure link below for specific Issuer requirements.
Retail investors
Accept investments from accredited and non-accredited investors alike, alongside institutional investors, trusts, and more.
Lower time-to-launch
Reg CF offerings can be prepared and launched in just a few weeks, provided an issuer has the right support during the process.
Early-stage funding
Inviting fans, followers, or customers to invest alongside traditional angels or VC can build a strong base of support.
Shares, SAFEs, and more
Whether you are offering common stock, preferred shares, or a SAFE note, Regulation CF can be your fundraising vehicle.
Rolling escrow closes
Once the target minimum offering amount is met and the deal has been live for 21 days, escrow can be closed regularly to deploy capital proceeds and fund your next phase of growth.
Note: Investors should weigh the risk of making investments, which includes the potential loss of your investment and the illiquid nature of non-public shares.